Influence of sand properties on sedimentation of heavy oil sands in submarine pipelines
-
摘要: 海底稠油管道中含砂可能会给管道与海上处理平台带来一系列问题。针对海管输送稠油携砂沉积问题,探究OLGA软件模拟固-液两相流的流态及沉积规律的可行性,并以某油田海底管道为研究对象,根据现场实际数据合理建模,分析砂粒粒径、含砂体积分数、休止角及砂粒密度对管道中的临界沉积速度与最大沉积位置的影响。结果表明:临界沉积速度随砂粒粒径增大先减小后增大,低含砂体积分数下临界砂沉积速度无明显变化,高含砂体积分数下临界砂沉积速度与含砂体积分数、砂密度正相关,与休止角负相关;最大砂沉积位置与砂粒粒径、砂密度负相关,与休止角正相关,含砂体积分数小于1%时最大砂沉积位置变化不明显,但高含砂体积分数对最大沉积位置的影响不可忽略。研究结果可为降低海管稠油输送过程中的安全风险提供参考。Abstract: The presence of sand in submarine heavy oil pipelines may bring a series of problems to the pipelines and offshore processing platforms. As for the sedimentation of sands contained in the heavy oil transported by submarine pipelines, the feasibility of simulating the solid-liquid two-phase flow pattern and the sedimentation laws of sands with the OLGA software was studied, and with the submarine pipelines of an oil field as the study object, a model was established reasonably based on the actual data. On this basis, the influence of the size, volume fraction, repose angle and density of sands on the critical settling velocity and the maximum settling location in the pipelines was analyzed. The results indicate that: The critical settling velocity decreases at first and then increases with the increasing of the sand size. The critical settling velocity varies little at low sand volume fraction, while it is of positive correlation with the volume fraction and density, of sands when it is high. Further, the maximum settling location was negatively correlated with sand particle size and density but positively correlated with the repose angle. When the volume fraction of sands is less than 1%, the change of the maximum settling location is not obvious, but the influence of high sand volume fraction on the maximum settling location cannot be ignored. Generally, the study results are expected to provide reference for the reduction of safety risks of heavy oil transportation in submarine pipelines.
-
据统计,中国海油近30年来在中国海域内共敷设有300余条海底管道,其中,继酸性成分与管道自身缺陷之后,出砂是导致海底管道失效的第三大影响因素[1]。砂沉积的危害主要表现为砂在管道设备内的积聚堵塞等。在海管长期运行过程中,砂沉积可能导致管道缩径、原油流通面积减小、压降增大、清管频率增大或卡球等问题[2-4],严重时甚至导致重大安全事故,使企业遭受巨大损失。
国内外学者对于不同条件下临界沉积速度的定义和描述各不相同,但本质上都是对砂粒随流体流动状态的表征[5-8]。目前,关于含砂管道输送问题的研究多以高含砂量、输送介质低黏度的工况为对象[9-10],而因存在试验系统成本昂贵、携砂流体状态难以控制等问题[11],对于较低含砂量、高黏原油长输海管砂沉积的研究较少。在此以旅大稠油为研究对象,其密度高、黏度大,地层出砂粒径小,一旦出砂严重或清理不及时,会对管道及海上处理平台造成危害。通过数值模拟研究海底管道在高黏输送介质、低含砂量条件下的砂沉积规律,预测不同影响因素下的管道临界沉积速度与最大沉积位置,以期降低砂沉积带来的安全风险。
1. 海管内砂粒受力分析
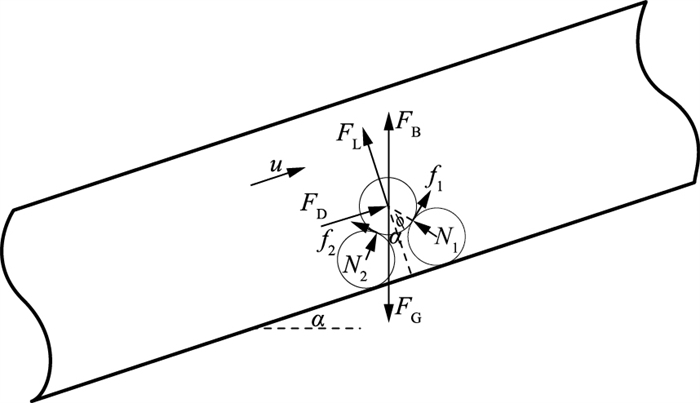
砂粒在运移过程中包括固定床、移动床及悬浮3种状态。为判断海底管道底部是否有砂沉积层出现,需对砂粒进行受力分析(图 1,FG为重力,FB为浮力,FL为升力,FD为曳力,f1、f2均为砂粒间摩擦力,N1、N2均为支持力,u为床层上方速度子层中的流体速度,α为管道倾角,ϕ为休止角)。砂粒滚动时不考虑法向应力和摩擦力的影响。
海管内砂粒所受重力、浮力、升力、曳力的计算式分别为:
FG=16ρsgπd3s (1) FB=16ρfgπd3s (2) FL=1.615ud2S√ρfμfdudy (3) FD=18CDρfu2d2s (4) 式中:ρs为砂粒密度,kg/m3;g为重力加速度,取9.81 m/s2;ds为砂粒直径,m;ρf为管输流体介质密度,kg/m3;μf为流体黏度,cP(1 cP=10-3 Pa·s);y为海管沿轴线方向的长度,m;CD为阻力系数。
当砂粒与其周围的流体存在速度差且流体的速度梯度垂直于砂粒的运动方向时,由于砂粒两侧的流速不一样,会产生一个由低速向高速方向的升力,即萨夫曼升力。
为使砂粒向上移动,需满足以下条件:
FLsinϕ+FDcosϕ>(FG−FB)sin(ϕ+α) (5) 为使粒子向下移动,需满足以下条件:
FLsinϕ+FDcosϕ<−(FG−FB)sin(ϕ−α) (6) 当沉积层表面剪切速率在数值上大于砂粒沉降速度时,砂粒开始悬浮流动:
v∗=√τfρf>vslcosα (7) 式中:v*为沉积层表面处流体的剪切速率,s-1;τf为剪切应力,N/m2;vsl为砂粒和流体之间的相对速度,m/s。
流体的流动状态可由雷诺数Re确定,当管内流体分别处于层流(Re<3)、过渡流(3<Re<300)、湍流(Re>300)条件下时,vsl的计算式分别为:
vsl=0.32673(ρs−ρf)(d2s/μf) (8) vsl=0.7086ds(ρs−ρf)0.667(ρfμf)−0.333 (9) vsl=2.9452(dsρs−ρfρf)0.5 (10) 砂粒的雷诺数Re可由下式计算得到:
Re=ρfvslds/μf (11) 采用Nielsen公式计算移动床的床层厚度和移动速度:
δsds=2.5τw−τw,c(ρs−ρf)gds (12) vb=4.8v∗−vslsinα (13) 式中:δs为移动床层的厚度,m;τw为壁剪应力,N/m2;τw,c为床层初始条件下的壁剪应力,N/m2;vb为移动床的轴向速度,m/s。
砂粒的体积分数计算基于稳态平流扩散方程:
ut=dcsdy=−vslcscosα (14) 式中:ut为涡黏系数;cs为悬浮砂粒的体积分数。
2. 模拟的可靠性验证
2.1 功能模块选择
PVTSim软件可根据输入的流体组分及其摩尔分数自动计算该流体的黏度、反常点等参数,也可手动输入试验测定的黏温关系、析蜡点、含蜡量等参数,校正系统的计算偏差,从而使模拟结果更加可靠。该软件中的Mix模块可将两种或两种以上的流体组分按照设定的比例混合,生成新的流体组分文件,新的流体组分文件不改变之前流体的类型。
OLGA是油气管道多相流动中常用的瞬态热工水力模拟软件,其中SIMPLE模型只考虑了管内砂粒的轴向运动,适用于评估管道中悬浮砂粒沿某一载体相的流动。相比SIMPLE模型,ADVANCED模型更加精确,考虑了床层的形成过程、不同流体间颗粒的截面分布以及轴向颗粒运移过程,适用于评估相间沉积和混合的情况,以下分析均采用ADVANCED模型。
2.2 可靠性试验验证
2.2.1 柴油携砂环道试验
隋冰[12]搭建了成品油携砂试验环道系统(表 1),分析管内砂粒的沉积运移状态,在此通过OLGA软件复现水平和上倾管路中的油携砂流态。
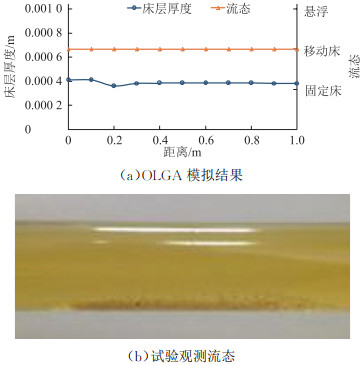
表 1 隋冰的成品油携砂试验条件参数试验介质 油品密度/(kg·m-3) 砂粒直径/目 油品黏度/(mPa·s) 砂粒密度/(kg·m-3) 管径/m 水、柴油、石英砂 819 30~40 2.4 2 650 0.025 模拟可知:在水平管道中砂粒质量分数为5%、流速小于0.1 m/s时,管道呈现稳定的移动床沉积状态,床层厚度约为单层颗粒直径,与试验结果相近(图 2)。砂粒运移过程中砂丘顶部颗粒会因流体的携带作用而脱离,因此砂粒团厚度逐渐减小,整体形状趋于扁平伸长。若流动条件无突变,砂粒最终会被流体携出管道。
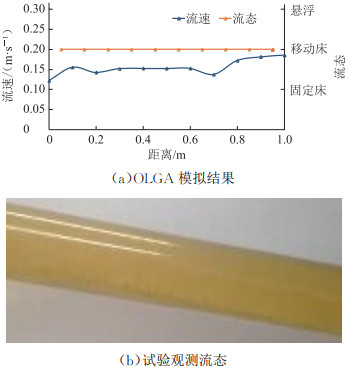
砂粒在管内运动时,主要受油流剪切、重力、管壁及颗粒间的摩擦作用,在水平管道中只需克服管壁及砂粒间的摩擦作用即可将砂粒清除,而在上倾管路中需克服重力和摩擦作用。在20°上倾管道中砂粒质量分数为10%、流速为0.15 m/s时,管道仍呈现移动床沉积状态,相比水平管路,倾斜管路中的砂粒更难被流体携走,因此当流速升高时仍可能保持原有的砂运移状态,模拟结果与试验结论一致(图 3)。
OLGA对于移动床流型的判别依赖于流体内的含砂体积分数,流体中所有砂粒均沉降至管底并向前移动时OLGA才会识别为移动床流型。
2.2.2 砂-水两相水平管道试验
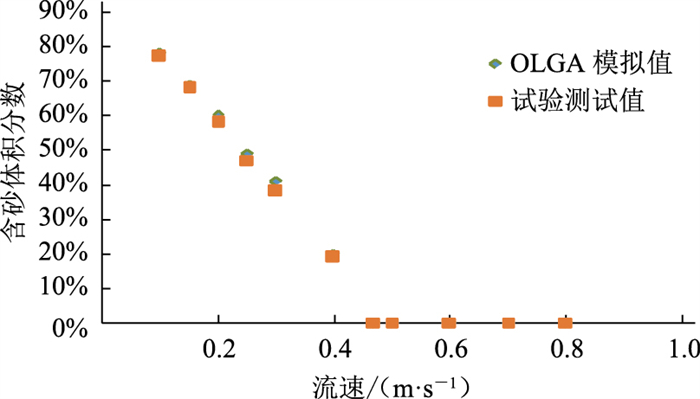
Danielson[13]于2007年开展了水平管道砂-水两相流动的临界条件试验(表 2),主要研究参数包括砂层厚度、含砂体积分数以及管段压降等。通过OLGA软件模拟得到相同试验条件下砂沉积床层高度、含砂体积分数及压降计算结果,并与试验值进行对比(表 3)。可见:水相流速与砂沉积量负相关,随着液相流速的增大,砂沉积量逐渐降低,OLGA模拟结果与试验吻合度较高。试验对床层厚度的判断以目测为主,而软件模拟可得到床层厚度的具体数值,相比试验研究具有一定优势。
表 2 Danielson的水平管道砂-水两相流动试验条件参数管径/m 管长/m 粒径/μm 含砂体积分数 液相流量/(m·s-1) 压力/MPa 0.069 215 280 30% 0.01~2 0.8 表 3 相同试验条件下OLGA模拟结果与试验数据对比情况水相流速/(m·s-1) 床层高度/m 含砂体积分数 相对误差 模拟值 试验值 0.10 0.050 78% 77% 1.28% 0.15 0.045 69% 68% 1.30% 0.20 0.040 60% 58% 2.70% 0.25 0.035 49% 47% 4.08% 0.30 0.030 41% 38% 6.17% 0.40 0.019 20% 19% 7.31% 0.50 0.000 0% 0% 0% 0.60 0.000 0% 0% 0% 0.70 0.000 0% 0% 0% 0.60 0.000 0% 0% 0% 0.70 0.000 0% 0% 0% OLGA模拟得到不同液体速度下流体含砂体积分数结果与试验数据吻合良好(图 4)。在流速约为0.47 m/s时含砂体积分数出现突变,一旦砂层开始形成,液相速度与砂沉积量负相关,0.47 m/s即为该条件下的临界沉积速度。
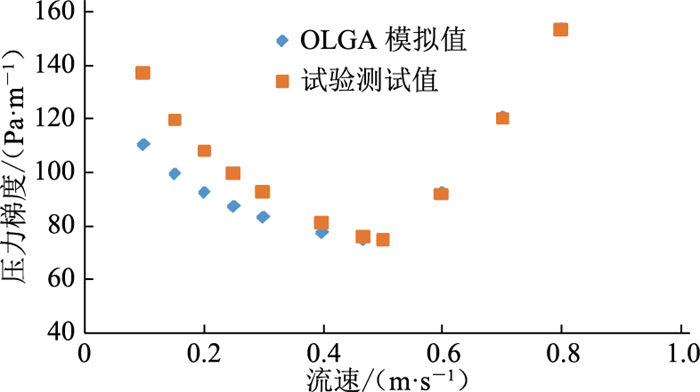
随着管内液相流速从0开始增大,压力梯度的斜率先负后正,压力梯度斜率零点在流速0.47 m/s附近,该流速即管段的临界沉积速度;低速条件下OLGA对于管内压降的预测值低于试验值,高速条件下两者吻合度较高(图 5)。以往研究表明,当压力梯度随液体流速的变化曲线斜率为负值(即图 5中流速小于0.47 m/s)时,管内多相流动可能会出现不稳定工况,例如段塞流和液体周期性累积等,这与移动床层的形成规律有明显的相似之处,当液相流速非常低时,砂床上方的流体从湍流转变为层流,沉积床层逐渐稳定[14]。
3. 海管砂沉积规律
3.1 模型建立
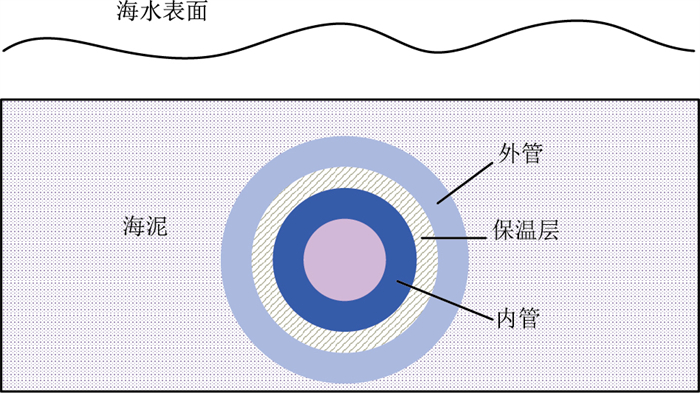
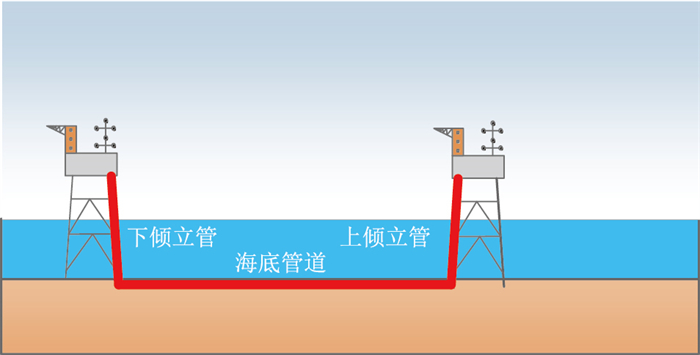
以渤海海域某油田管道为研究对象,该混输管道长15 606 m,采用双层钢管+保温层结构,管道埋深(管道顶端至海泥面)1.5 m,在平台间呈下倾-水平-上倾敷设,立管处近乎垂直,且立管长度相比海底管道长度数量级较低。模拟得知在立管处几乎无沉积层,为提高计算效率,仅选取管道全程中的水平段建立模型(图 6、图 7、表 4)。
表 4 某油田海底管道基础模拟条件参数管径/m 黏度/(mPa·s) 粒径/m 含砂体积分数 休止角/(°) 砂密度/(kg·m-3) 0.254 678.2 0.000 1 0.05% 30 2 000 3.2 砂粒特征的影响
3.2.1 粒径
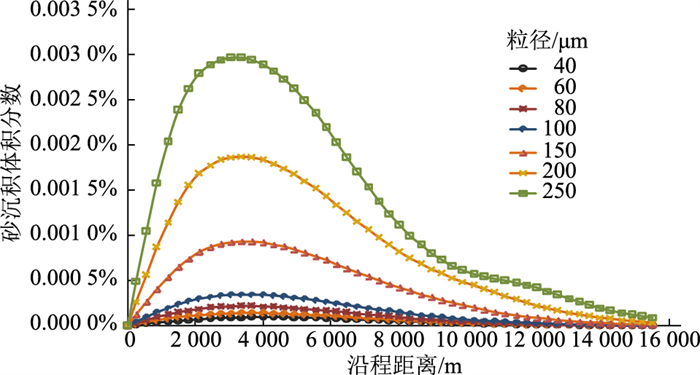
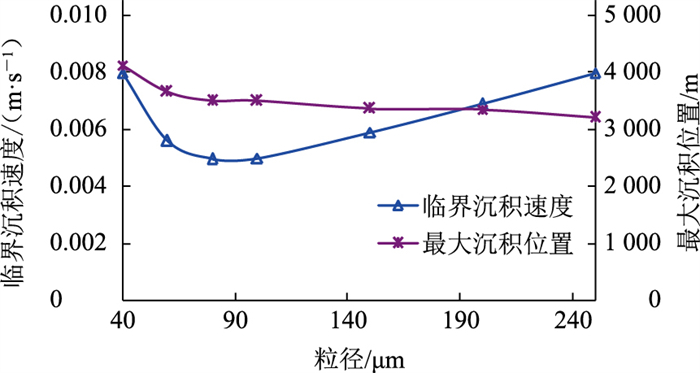
其他基础条件不变,选取粒径40~250 μm的砂粒进行模拟(图 8、图 9)。随着砂粒粒径不断增大,管道临界沉积速度并非线性变化,而是先减小后增大,在80~100 μm之间存在一临界粒径使得管道沉积难度明显增大,可见粒径变化对沉积规律的影响较为复杂。管道沿线砂沉积量均呈现先增大后减小的规律,且最大沉积位置与粒径变化负相关[15]。当砂粒粒径增大时,砂粒之间碰撞加剧,单一砂粒所受阻力增加,产生更大的动能损失,在沉积概率相同的条件下沉积量增大。砂粒运动至某一位置后与之前发生碰撞的砂粒相遇聚集,动能逐渐减小,大部分砂粒于最高沉积位置沉积,少部分未发生碰撞或碰撞不完全的砂粒继续被流体介质携带,直至全部沉积。
3.2.2 含砂体积分数
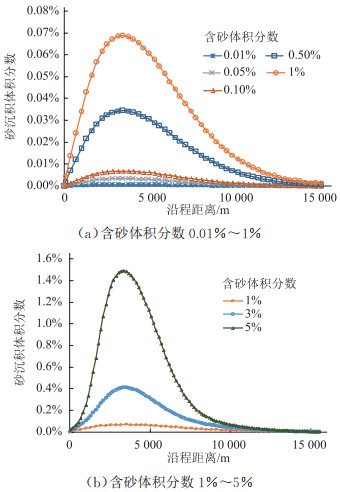
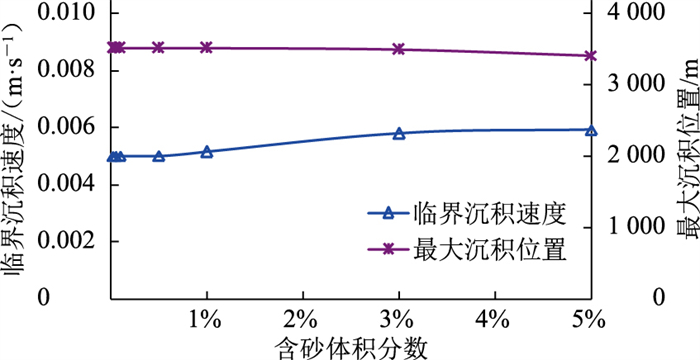
其他计算条件不变,为贴合实际管道稠油低出砂量工况,选取0.01%、0.05%、0.1%、0.5%、1%、3%、5%等7种不同含砂体积分数的工况进行模拟(图 10、图 11)。当管道稳定运行后,沿水平管段方向砂沉积量先逐渐增大,达到最高值后逐渐下降。随着海管入口含砂体积分数的增大,相同位置处砂沉积体积分数显著增大,在低砂工况下最大沉积位置均位于距海管起点3 508.53 m处;但当含砂体积分数逐渐增至5%时,临界沉积速度与含砂体积分数正相关,最大沉积位置与含砂体积分数负相关,砂粒间的相互作用增强,流场中需要更多能量来维持砂粒运移。由此可见,当含砂体积分数较低时,管内临界沉积速度及最大沉积位置主要取决于流场中的其他条件,而当含砂体积分数增至某一值后其影响不可忽略[16-18]。
3.2.3 休止角
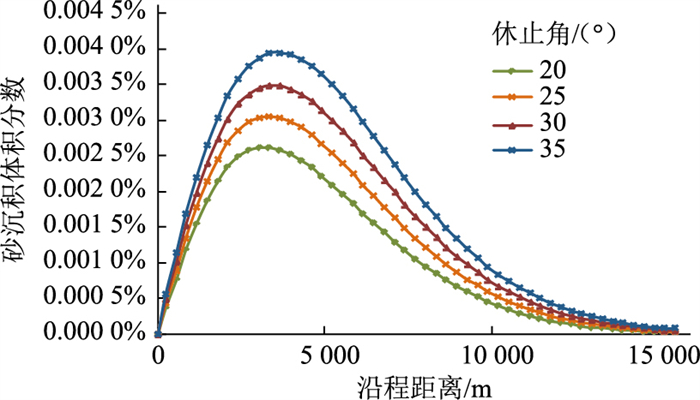
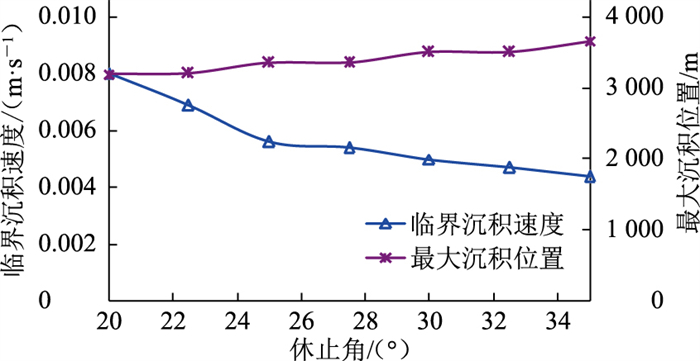
其他计算条件不变,选取砂粒休止角分别为20°、25°、30°、35°的工况进行模拟(图 12、图 13)。休止角是砂粒内摩擦力的外在表现[19],可通过试验进行参数标定,在OLGA计算中可作为变量自行输入,一般休止角越大,砂粒形状与球形偏差越大[20]。相比球形砂粒,不规则砂粒所受曳力较大,在相同条件下更容易被流体携带,对应的临界沉积速度更小,最大沉积位置向后移动。
3.2.4 砂密度
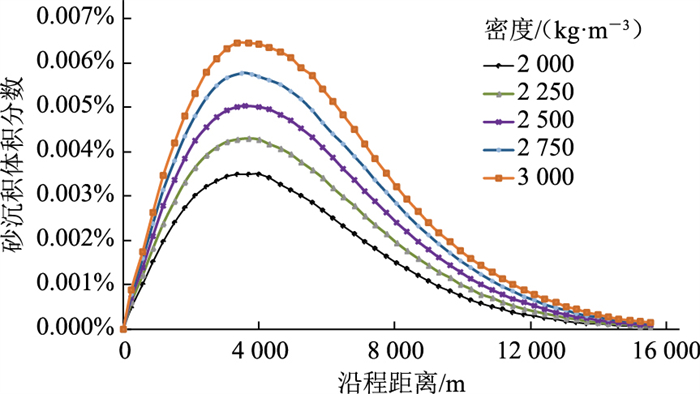
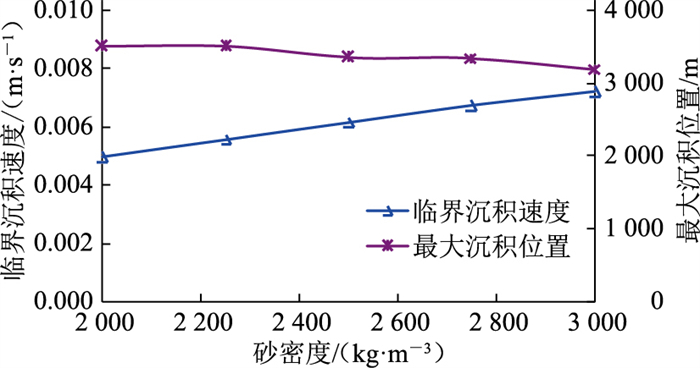
其他计算条件不变,选取砂粒密度分别为2 000 kg/m3、2 250 kg/m3、2 500 kg/m3、2 750 kg/m3、3 000 kg/m3进行模拟(图 14、图 15)。砂粒密度越大,单个砂粒所受重力与阻力的合力越大,当两者合力大于流体曳力时即出现沉降现象。砂粒密度增大将导致沉降临界沉积速度增大,最大沉积量位置靠前,但改变砂粒密度不会导致流场突变,因此其影响有限[21]。
4. 结论
(1)以某海上出砂稠油管道为研究对象,根据现场数据合理建模,基于不同砂粒粒径、含砂量、砂粒休止角及砂密度的砂粒属性特征进行模拟,分析海底管道的砂沉积规律。OLGA软件中ADVANCED模型的预测结果与相关试验结果吻合度较高,验证了模型的高精度。
(2)临界沉积速度随砂粒粒径增大先减小后增大;流体中含砂体积分数较小时管内临界砂沉积速度无明显变化,流体中含砂体积分数较大时管内临界砂沉积速度与含砂体积分数正相关;砂临界沉积速度与休止角负相关,与砂密度正相关。管道内砂最大沉积位置与砂粒粒径、密度负相关;含砂体积分数较小时其值对砂最大沉积位置影响不明显,但含砂体积分数较大时其影响不可忽略;休止角与砂的最大沉积位置正相关。
(3)研究主要分析了砂粒自身属性对长输水平管道砂沉积特性的影响,为解决油气开发与输送过程中由出砂而引起的安全问题提供了指导。今后在该领域的研究中,流体性质与管道结构对砂沉积的影响也值得关注。
-
表 1 隋冰的成品油携砂试验条件参数
试验介质 油品密度/(kg·m-3) 砂粒直径/目 油品黏度/(mPa·s) 砂粒密度/(kg·m-3) 管径/m 水、柴油、石英砂 819 30~40 2.4 2 650 0.025 表 1 隋冰的成品油携砂试验条件参数
试验介质 油品密度/(kg·m-3) 砂粒直径/目 油品黏度/(mPa·s) 砂粒密度/(kg·m-3) 管径/m 水、柴油、石英砂 819 30~40 2.4 2 650 0.025 表 2 Danielson的水平管道砂-水两相流动试验条件参数
管径/m 管长/m 粒径/μm 含砂体积分数 液相流量/(m·s-1) 压力/MPa 0.069 215 280 30% 0.01~2 0.8 表 2 Danielson的水平管道砂-水两相流动试验条件参数
管径/m 管长/m 粒径/μm 含砂体积分数 液相流量/(m·s-1) 压力/MPa 0.069 215 280 30% 0.01~2 0.8 表 3 相同试验条件下OLGA模拟结果与试验数据对比情况
水相流速/(m·s-1) 床层高度/m 含砂体积分数 相对误差 模拟值 试验值 0.10 0.050 78% 77% 1.28% 0.15 0.045 69% 68% 1.30% 0.20 0.040 60% 58% 2.70% 0.25 0.035 49% 47% 4.08% 0.30 0.030 41% 38% 6.17% 0.40 0.019 20% 19% 7.31% 0.50 0.000 0% 0% 0% 0.60 0.000 0% 0% 0% 0.70 0.000 0% 0% 0% 0.60 0.000 0% 0% 0% 0.70 0.000 0% 0% 0% 表 3 相同试验条件下OLGA模拟结果与试验数据对比情况
水相流速/(m·s-1) 床层高度/m 含砂体积分数 相对误差 模拟值 试验值 0.10 0.050 78% 77% 1.28% 0.15 0.045 69% 68% 1.30% 0.20 0.040 60% 58% 2.70% 0.25 0.035 49% 47% 4.08% 0.30 0.030 41% 38% 6.17% 0.40 0.019 20% 19% 7.31% 0.50 0.000 0% 0% 0% 0.60 0.000 0% 0% 0% 0.70 0.000 0% 0% 0% 0.60 0.000 0% 0% 0% 0.70 0.000 0% 0% 0% 表 4 某油田海底管道基础模拟条件参数
管径/m 黏度/(mPa·s) 粒径/m 含砂体积分数 休止角/(°) 砂密度/(kg·m-3) 0.254 678.2 0.000 1 0.05% 30 2 000 表 4 某油田海底管道基础模拟条件参数
管径/m 黏度/(mPa·s) 粒径/m 含砂体积分数 休止角/(°) 砂密度/(kg·m-3) 0.254 678.2 0.000 1 0.05% 30 2 000 -
[1] 王红红, 刘国恒. 中国海油海底管道事故统计及分析[J]. 中国海上油气, 2017, 29(5): 157-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201705022.htm WANG H H, LIU G H. Statistics and analysis of subsea pipeline accidents of CNOOC[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2017, 29(5): 157-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201705022.htm
[2] 王威, 鲁瑜, 罗峰, 张宗超, 郭庆. 海底长输油管道缩径模拟实验及计算分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(5): 181-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201705031.htm WANG W, LU Y, LUO F, ZHANG Z C, GUO Q. Simulation experiment and calculation analysis of submarine long-distance oil pipeline[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(5): 181-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201705031.htm
[3] 王飞, 王运, 郑利军, 王立佳, 王凯. 携砂管流临界输运特性研究进展[J]. 北京石油化工学院学报, 2018, 26(2): 45-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJSY201802010.htm WANG F, WANG Y, ZHENG L J, WANG L J, WANG K. Research advances in critical transport characteristics of pipe flow with sand[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Petro-Chemical Technology, 2018, 26(2): 45-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJSY201802010.htm
[4] MENDOZA L, MARIN M, NASCIMENTO C M, PERAZA R. Sand transport modeling in heavy oil gathering network in Orinoco oil belt, Venezuela[C]. Calgary: SPE Canada Heavy Oil Technical Conference, 2017: SPE-184968-MS.
[5] DORON P, BARNEA D. Flow pattern maps for solid-liquid flow in pipes[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1996, 22(2): 273-283. doi: 10.1016/0301-9322(95)00071-2
[6] CHEREMISINOFF N P. Properties and concepts of single fluid flows[M]//CHEREMISINOFF N P. Encyclopedia of Fluid Mechanics. Houston: Gulf Publishing Company, 1986: 227-352.
[7] HILL A L. Determine the critical flow rates for low concentration sand transport in two-phase pipe flow by experimentation and modeling[D]. Tulsa: The University of Tulsa, 2011.
[8] 石凯月, 何利民, 罗小明, 静玉晓, 杨东海, 李清平, 等. 管道砂沉积与流体携砂临界速度研究进展及展望[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(3): 188-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201803026.htm SHI K Y, HE L M, LUO X M, JING Y X, YANG D H, LI Q P, et al. Research progress and prospect of sand deposition and sand transportation critical velocities in pipelines[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(3): 188-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201803026.htm
[9] AL-LABABIDI S, YAN W, YEUNG H. Sand transportations and deposition characteristics in multiphase flows in pipelines[J]. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 2012, 134(3): 034501. doi: 10.1115/1.4006433
[10] YAN W. Sand transport in multiphase pipelines[D]. Cranfield: Cranfield University, 2010.
[11] 黄芳飞, 林德才, 王博, 陈晨, 吴海浩, 康琦, 等. 多相混输临界携砂速度研究进展[J]. 油气储运, 2019, 38(11): 1201-1211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCY201911001.htm HUANG F F, LIN D C, WANG B, CHEN C, WU H H, KANG Q, et al. Research progress on the critical sand carrying velocity of multiphase mixed transport[J]. Oil & Gas Storage and Transportation, 2019, 38(11): 1201-1211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCY201911001.htm
[12] 隋冰. 成品油管道油携杂质流动特性研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2015. SUI B. Study on flow characteristics of impurity entrained by oil in product oil pipeline[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2015.
[13] DANIELSON T J. Sand transport modeling in multiphase pipelines[J]. Houston: Offshore Technology Conference, 2007: OTC-18691-MS.
[14] 闫容菊, 王卫强, 李梓萌, 伍盛一, 杨小辰. 海洋立管系统严重段塞流研究进展[J]. 辽宁石油化工大学学报, 2017, 37(5): 26-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSSX201705006.htm YAN R J, WANG W Q, LI Z M, WU S Y, YANG X C. Progress of severe slugging in marine riser system[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Petroleum & Chemical Technology, 2017, 37(5): 26-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSSX201705006.htm
[15] NAJMI K, MCLAURY B S, SHIRAZI S A, CREMASCHI S. Experimental study of low concentration sand transport in wet gas flow regime in horizontal pipes[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 24: 80-88.
[16] NAJMI K, MCLAURY B S, SHIRAZI S A, CREMASCHI S A. Experimental study of low concentration sand transport in low liquid loading water-air flow in horizontal pipes[C]. Banff: 9th North American Conference on Multiphase Technology, 2014: BHR-2014-A2.
[17] NAJMI K, MCLAURY B S, SHIRAZI S A, CREMASCHI S. The effect of viscosity on low concentration particle transport in single-phase (liquid) horizontal pipes[J]. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 2016, 138(3): 032902.
[18] NAJMI K, HILL A L, MCLAURY B S, SHIRAZI S A, CREMASCHI S. Experimental study of low concentration sand transport in multiphase air-water horizontal pipelines[J]. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 2015, 137(3): 032908.
[19] 张克博. 岩屑颗粒沉降阻力及其休止角计算模型[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2019. ZHANG K B. The calculation model of cutting particles settling drag and its reciprocation angle[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2019.
[20] 王胤, 艾军, 杨庆. 考虑粒间滚动阻力的CFD-DEM流-固耦合数值模拟方法[J]. 岩土力学, 2017, 38(6): 1771-1780. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201706027.htm WANG Y, AI J, YANG Q. A CFD-DEM coupled method incorporating soil inter-particle rolling resistance[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(6): 1771-1780. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201706027.htm
[21] 张文欣, 周晓红, 陈宏举. 海底管道砂沉积模拟研究[J]. 石油化工高等学校学报, 2016, 29(1): 86-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHX201601017.htm ZHANG W X, ZHOU X H, CHEN H J. Numerical simulation of sand depositional rule in subsea multiphase pipeline[J]. Journal of Petrochemical Universities, 2016, 29(1): 86-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHX201601017.htm




 下载:
下载: